Crosscutting Concepts
Consider using one of the below as a lens through which to explore content featured in the full film. Remember that this will affect the specific learning outcome for your students; don't aim to use all three!
- Energy and Matter
- Cause and Effect
- Systems and System Models
Disciplinary Core Ideas
Depending on your grade level and subject matter, your expected use of the full film will undoubtedly differ from other K-12 teachers. Here we list the scientific ideas that shine through in Habitat Earth. Considering focusing on one or more.
Grade 3
» Life Science
- LS4.C: Adaptation
- For any particular environment, some kinds of organisms survive well, some survive less well, and some cannot survive at all.
- LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans
- Populations live in a variety of habitats, and change in those habitats affects the organisms living there.
Grade 4
» Earth and Space Science
- ESS2.E: Biogeology
- Living things affect the physical characteristics of their regions.
Grade 5
» Life Science
- LS2.A: Interdependence Relationships in Ecosystems.
- The food of almost any kind of animals can be traced back to plants. Organisms are related in food webs. Organisms called decomposers break down dead organisms, recycling some materials back into the soil. A healthy ecosystem is one in which multiple species are able to meet their needs, and newly introduced species can damage the balanceof an ecosystem.
- LS2.B: Cycles of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
- Matter cycles between the air and soil and among plants, animals, and microbes as these organisms live and die.
» Earth and Space Science
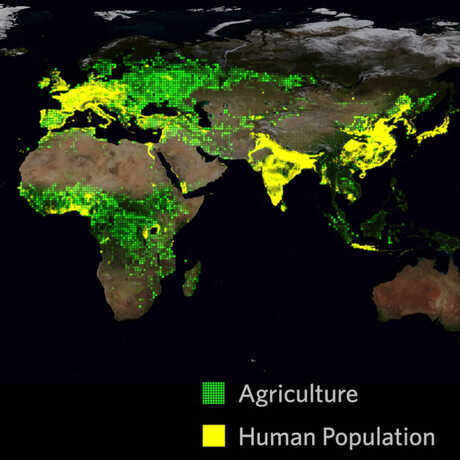
- ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
- Human activities have had major effects on the land, vegetation, streams, ocean, and air. But individuals and communities are doing things to help protect Earth’s resources and environments.
Middle School
» Life Science
- LS1.C: Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms
- Plants, algae (including phytoplankton), and many microorganisms use energy from light to make sugars through the process of photosynthesis.
- LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems
- Organisms, and populations of organisms, are dependent on their environmental interactions both with other living things and with nonliving factors.
- LS2.B: Cycles of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
- Food webs are models that demonstrate how matter and energy is transferred between produces, consumers and decomposers.
- LS2.C: Ecosystem Dynamics, Functioning, and Resilience
- Ecosystems vary overtime; disruptions to physical or biological components can lead to shifts in all its populations.
- LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans
- Changes in biodiversity can influence humans’ resources.
» Earth and Space Science
- ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
- Water continually cycles among land, ocean, and atmosphere.
- ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
- Human activities have significantly altered the biosphere.
High School
» Life Science
- LS1.C: Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms
- The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy.
- LS2.C: Ecosystem Dynamics, Functioning, and Resilience
- Anthropogenic changes in the environment can disrupt an ecosystem and threaten the survival of some species.
- LS4.C: Adaptation
- Changes in the physical environment, whether naturally occurring or human induced, have contributed to the expansion of some species, emergence of new species and decline—and sometimes extinction—of some species.
- LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans
- Humans depend on the living world for the resources and other benefits provided by biodiversity. Human activity is also having adverse impacts on biodiversity. Sustaining biodiversity is essential to supporting and enhancing life on Earth.
» Earth and Space Science
- ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
- The sustainability of human societies and the biodiversity that supports them requires responsible management of natural resources.
- ESS3.D: Global Climate Change
- Though the magnitudes of human impacts are greater than they have ever been, so too are human abilities to model, predict, and manage current and future impacts. Important discoveries are still being made about how the ocean, the atmosphere, and the biosphere interact and are modified in response to human activities.